Enjoy this Article, Statistics, Insights and Much More...
Genital Size

Continue Reading your
Article with a Genital Size
Subscription.
Explore our Subscription Plans
More Coverage
Understanding Erectile Dysfunction: Causes, Impact, and Treatment
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a common condition that affects millions of men worldwide. This article delves into the causes, impact, and treatment options for ED, including physical, psychological, and lifestyle factors, as well as which ethnic groups are most affected.
Two Vaginas: Understanding Uterus Didelphys and Embracing Self-Acceptance
Discover the physical and emotional challenges of uterus didelphys, and how women can embrace their unique physical traits.
The Truth About Vaginal Wetness: What It Means and How to Deal with It
Discover the natural causes of vaginal wetness and how to handle it comfortably and discreetly in any situation.
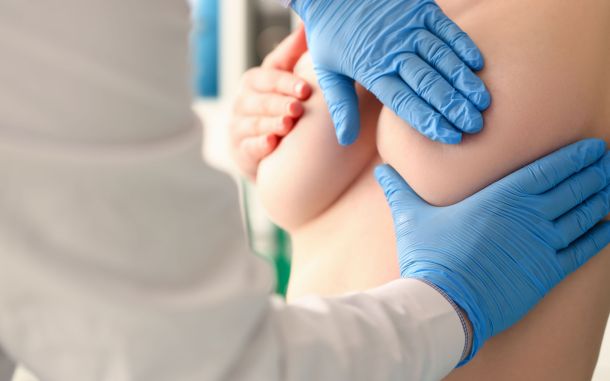
Demystifying the Medical Breast Exam: What to Expect and How to Feel Prepared
Discover what to expect during a medical breast exam, how it's conducted, and how to prepare properly, enabling you to approach the appointment with confidence and prioritize breast health.